Inulin
Inulin
Inulin is a type of soluble fiber and prebiotic. It cannot be digested or absorbed in the stomach but it will stay in the bowel and feed the good bacteria in the gut 1. Inulin is a fructose molecule found in a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, and herbs, including wheat, onions, bananas, leaks, artichokes, and asparagus. Most inulin used in supplements comes from soaking chicory roots in hot water 2.
Fun Facts
Today, inulin is widely used in functional foods throughout the world for their health properties and technological properties 3. From dietary supplements to infant formula, from drinks to various pastries, inulin appears more and more in our life. Because of its creamy consistency after dissolving in water, manufacturers add inulin as a fat substitute in margarine and salad dressing, and replace sugar in some processed products 4.
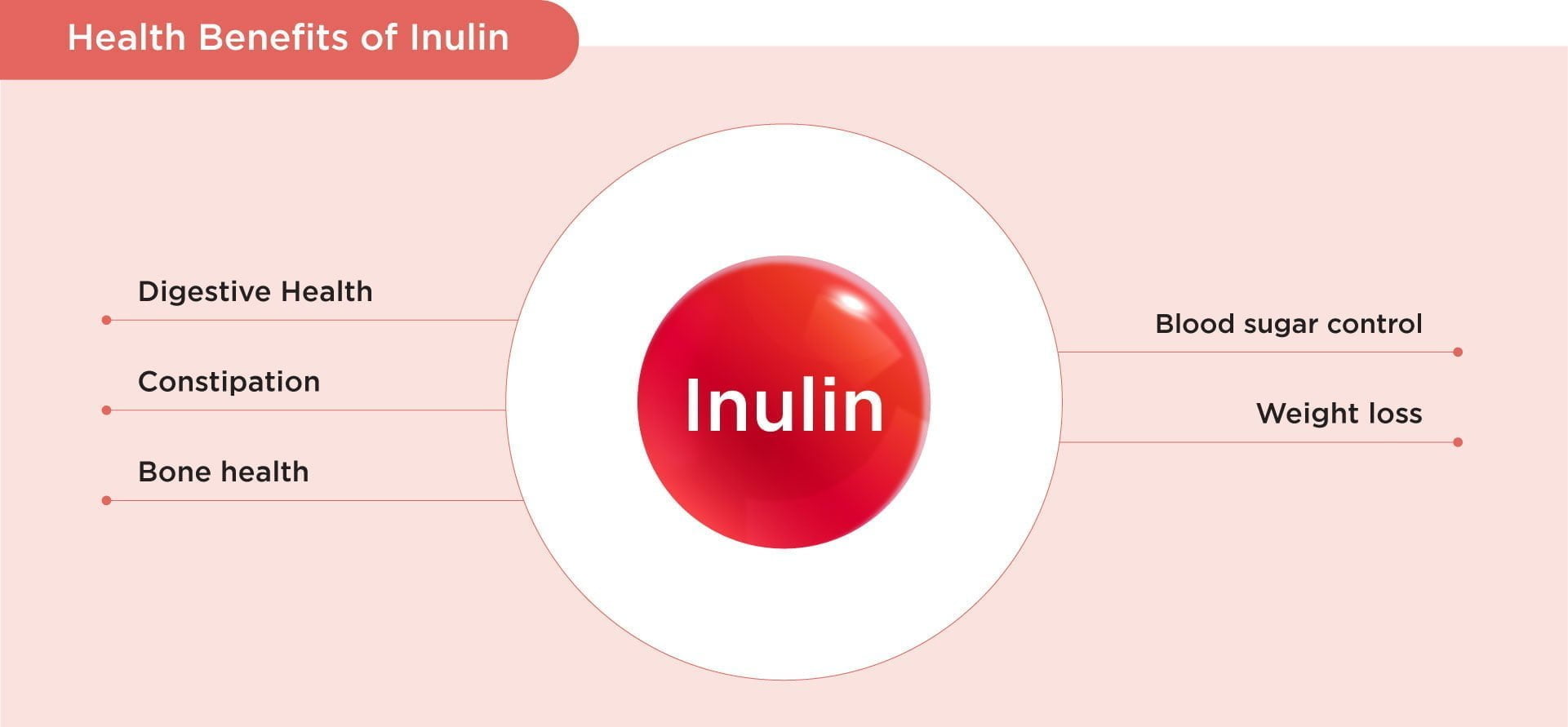
Published Health Benefits
1. Digestive Health
- Inulin slows digestion, increases fullness and reduces cholesterol absorption as it passes through the digestive tract 5.
- Inulin helps to increase the amount of healthful bacteria, particularly Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli which helps to improve digestion, immunity and overall health 6.
2. Constipation
- Inulin enables the body to have better absorption of nutrients from food. Studies have shown that those who consumed inulin experienced more frequent bowel movements and improved stool consistency 7.
3. Bone health
- Inulin enhances calcium and magnesium absorption from the gut, which contributes to increased bone density 8.
4. Blood sugar control
- Studies proved that supplementation with inulin can reduce blood sugar levels for middle-aged people and the elderly 9,10.
- Inulin slows the digestion of carbohydrates, allowing sugar to be released slowly and therefore preventing a drastic spike in blood sugar level after food 11. Moreover, the sweetness of inulin is only one-tenth of sucrose.
5. Weight loss
- As a dietary fiber, inulin contains no calories and provides satiety, which can help to curb appetite, beneficial to those on diet 12.
- In addition, inulin can reduce the inflammatory response in obese people 12.
Recommendation Daily Dose
There is no official dose for inulin. Some sources suggest starting with 2-3g per day for at least 1-2 weeks and slowly increase the dose to 5-10g per day 1.
References:
1. Spritzler, F. (2020). Inulin (a prebiotic fiber): Health benefits and risks. Retrieved 27 September 2021, from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318593
2. INULIN: Overview, Uses, Side Effects, Precautions, Interactions, Dosing and Reviews. (2021). Retrieved 27 September 2021, from https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1048/inulin
3. Niness K. R. (1999). Inulin and oligofructose: what are they?. The Journal of nutrition, 129(7 Suppl), 1402S–6S. doi: 10.1093/jn/129.7.1402S
4. Slavin J. (2013). Fiber and prebiotics: mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients, 5(4), 1417–1435. doi: 10.3390/nu5041417
5. Shoaib, M., Shehzad, A., Omar, M., Rakha, A., Raza, H., & Sharif, H. et al. (2016). Inulin: Properties, health benefits and food applications. Carbohydrate Polymers, 147, 444-454. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.020
6. Vandeputte, D., Falony, G., Vieira-Silva, S., Wang, J., Sailer, M., & Theis, S. et al. (2017). Prebiotic inulin-type fructans induce specific changes in the human gut microbiota. Gut, 66(11), 1968-1974. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313271
7. Collado Yurrita, L., San Mauro Martín, I., Ciudad-Cabañas, M. J., Calle-Purón, M. E., & Hernández Cabria, M. (2014). Effectiveness of inulin intake on indicators of chronic constipation; a meta-analysis of controlled randomized clinical trials. Nutricion hospitalaria, 30(2), 244–252. doi: 10.3305/nh.2014.30.2.7565
8. García-Vieyra, M., Del Real, A., & López, M. (2014). Agave Fructans: Their Effect on Mineral Absorption and Bone Mineral Content. Journal Of Medicinal Food, 17(11), 1247-1255. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2013.0137
9. Cai, X., Yu, H., Liu, L., Lu, T., Li, J., Ji, Y., Le, Z., Bao, L., Ma, W., Xiao, R., & Yang, Y. (2018). Milk Powder Co-Supplemented with Inulin and Resistant Dextrin Improves Glycemic Control and Insulin Resistance in Elderly Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 12-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Molecular nutrition & food research, 62(24), e1800865. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201800865
10. Roshanravan, N., Mahdavi, R., Alizadeh, E., Jafarabadi, M. A., Hedayati, M., Ghavami, A., Alipour, S., Alamdari, N. M., Barati, M., & Ostadrahimi, A. (2017). Effect of Butyrate and Inulin Supplementation on Glycemic Status, Lipid Profile and Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Level in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Hormone and metabolic research = Hormon- und Stoffwechselforschung = Hormones et metabolisme, 49(11), 886–891. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-119089
11. Guess, N. D., Dornhorst, A., Oliver, N., & Frost, G. S. (2016). A Randomised Crossover Trial: The Effect of Inulin on Glucose Homeostasis in Subtypes of Prediabetes. Annals of nutrition & metabolism, 68(1), 26–34. doi: 10.1159/000441626
12. Perrigue, M. M., Monsivais, P., & Drewnowski, A. (2009). Added soluble fiber enhances the satiating power of low-energy-density liquid yogurts. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 109(11), 1862–1868. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2009.08.018